

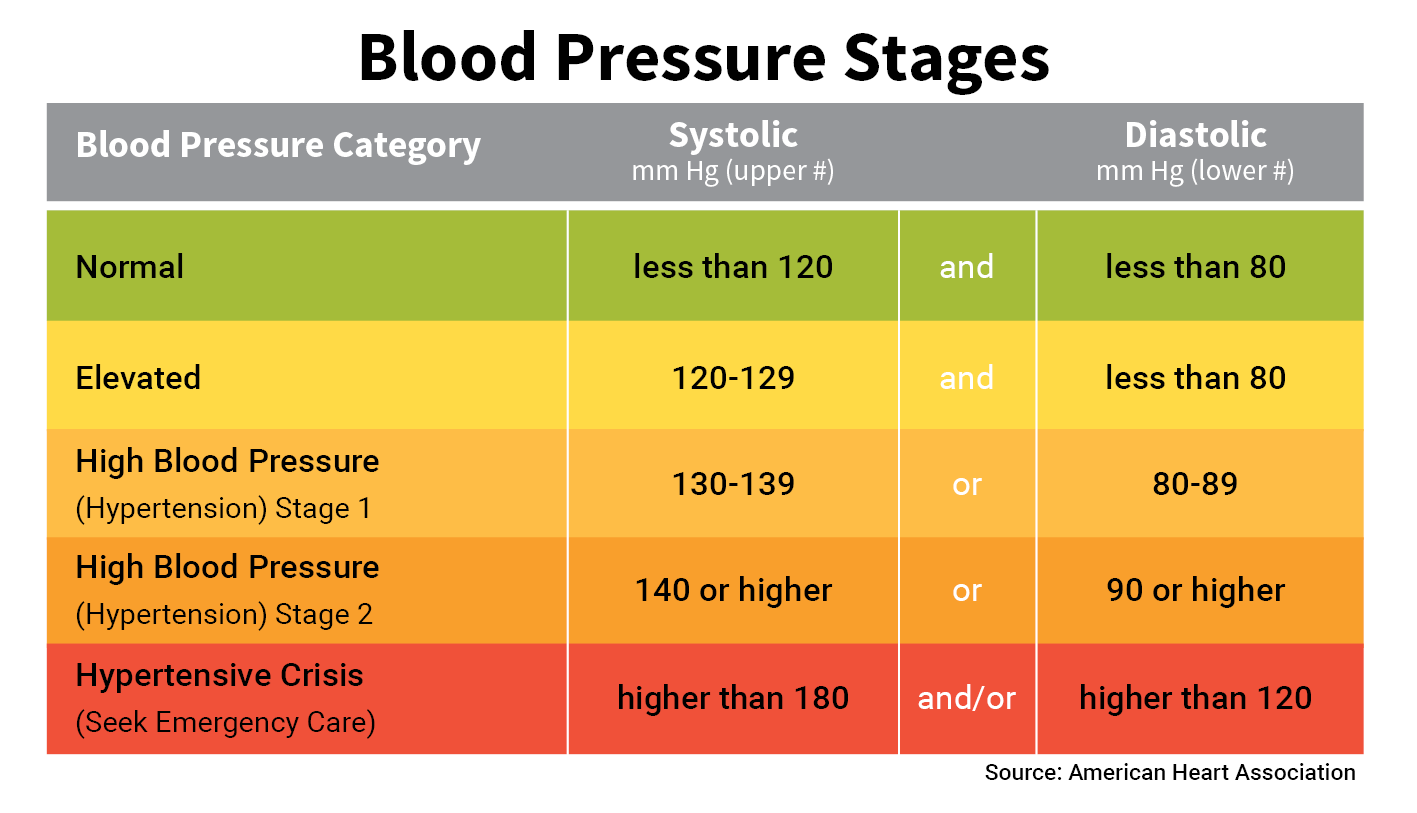
There is an ongoing medical debate over what is the optimal level of blood pressure to target when using drugs to lower blood pressure with hypertension, particularly in older people. Observational studies demonstrate that people who maintain arterial pressures at the low end of these pressure ranges have much better long-term cardiovascular health. The risk of cardiovascular disease increases progressively above 115/75 mmHg, below this level there is limited evidence. The same classification is used for all ages from 16 years.Ī BP category is defined according to seated clinic BP and by the highest level of BP, whether systolic or diastolic.ī Isolated systolic hypertension is graded 1, 2, or 3 according to systolic BP values in the ranges indicated.
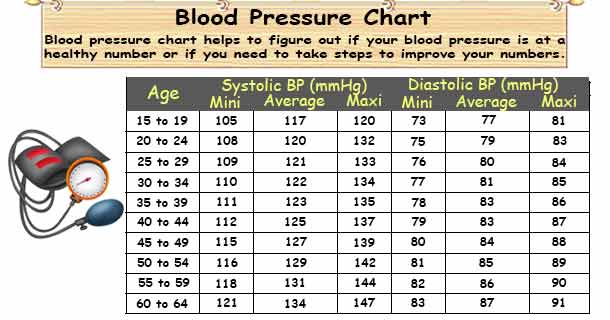
Long-term hypertension is more common than long-term hypotension. Long-term hypertension is a risk factor for many diseases, including stroke, heart disease, and kidney failure. Both hypertension and hypotension have many causes and may be of sudden onset or of long duration. In the short term, blood pressure is regulated by baroreceptors, which act via the brain to influence the nervous and the endocrine systems.īlood pressure that is too low is called hypotension, pressure that is consistently too high is called hypertension, and normal pressure is called normotension. īlood pressure is influenced by cardiac output, systemic vascular resistance and arterial stiffness and varies depending on situation, emotional state, activity, and relative health/disease states. Most of these semi-automated methods measure blood pressure using oscillometry. Early automated alternatives to mercury-tube sphygmomanometers were often seriously inaccurate, but modern devices validated to international standards achieve an average difference between two standardized reading methods of 5 mm Hg or less, and a standard deviation of less than 8 mm Hg. However, semi-automated methods have become common, largely due to concerns about potential mercury toxicity, although cost, ease of use and applicability to ambulatory blood pressure or home blood pressure measurements have also influenced this trend. Auscultation is still generally considered to be the gold standard of accuracy for non-invasive blood pressure readings in clinic. Traditionally, blood pressure was measured non-invasively using auscultation with either an aneroid gauge, or a mercury-tube sphygmomanometer. 127/79 mmHg in men and 122/77 mmHg in women, although these average data mask significantly diverging regional trends. Globally, the average blood pressure, age standardized, has remained about the same since 1975 to the present, at approx. Normal resting blood pressure, in an adult is approximately 120 millimetres of mercury (16 kPa) systolic over 80 millimetres of mercury (11 kPa) diastolic, denoted as "120/80 mmHg". It is measured in millimeters of mercury ( mmHg) above the surrounding atmospheric pressure.īlood pressure is one of the vital signs-together with respiratory rate, heart rate, oxygen saturation, and body temperature-that healthcare professionals use in evaluating a patient's health. Blood pressure is usually expressed in terms of the systolic pressure (maximum pressure during one heartbeat) over diastolic pressure (minimum pressure between two heartbeats) in the cardiac cycle. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" refers to the pressure in the large arteries. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. A healthcare worker measuring blood pressure using a sphygmomanometer.īlood pressure ( BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
